5 REASONS WHY ERBIUM:YAG LASERS OUTPERFORM CO2 LASERS
1. An Erbium : YAG laser wavelength is optimal for skin ablation.
Erbium:YAG lasers are optimal for skin ablation primarily because of the wavelength this technology generates. Erbium:YAG is emitted at 2,940 nm, while CO2 has a much longer wavelength at 10,600 nm. Chromophore absorption curves show a significant bump in the water absorption coefficient between 2,500-3,500 nm and a drop down at 7,500-20,000 nm.

Erbium:YAG lasers have a very efficient beam to target water and relatively limited hemoglobin absorption. Because water is such a critical component in the epidermal and dermal tissue, the 2,940 nm wavelength produced by Erbium:YAG lasers is capable of rapidly vaporizing water residing in the skin. This unique wavelength delivers an almost instant skin ablation while limiting heat damage in the surrounding area.
This thermal damage is the biggest difference between Erbium and Carbon Dioxide lasers. Carbon Dioxide lasers have been used to treat and ablate the skin since the 1970s. However, because the absorption in skin tissue is relatively low compared to Erbium lasers (in both water and hemoglobin), their result is substantial excess heat in the surrounding tissue. The consequences of that are localized necrosis (tissue death that leads to slower recovery time), more post-treatment discomfort, and greater instances of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), all while not necessarily allowing for better results when compared to Erbium lasers.
2. Erbium:YAG lasers can vary their treatment depths (full skin resurfacing vs. light Celebrity Peel).
Again, the varied treatment depths of Er:YAG lasers are mostly credited to the significantly greater absorption in water found in the epidermal and dermal tissue. This significant water absorption allows practitioners to reduce the pulse duration to make the treatment “colder” (i.e., pulse duration at 100 microseconds), or extend the pulse duration for a warmer therapy (up to 1000 microseconds).
A “cold laser” treatment performs laser therapy that doesn’t cause significant thermal damage to the tissue. CO2 technology can’t provide the same treatment because the thermal damage inherent in the wavelength of 10,600 nm makes it incredibly difficult (or impossible) to treat a patient without heating the tissue. Practitioners using Er:YAG lasers are afforded the option to cater treatments to each patient better and can elect to build thermal damage by increasing the pulse duration, or keeping those thermal effects limited.
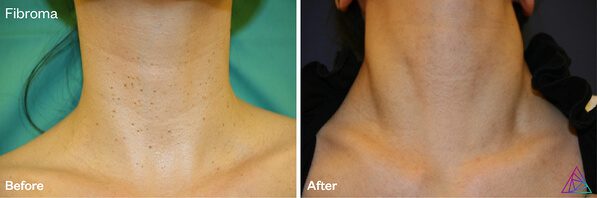
3. Erbium:YAG laser treatments create less thermal damage and are less painful.
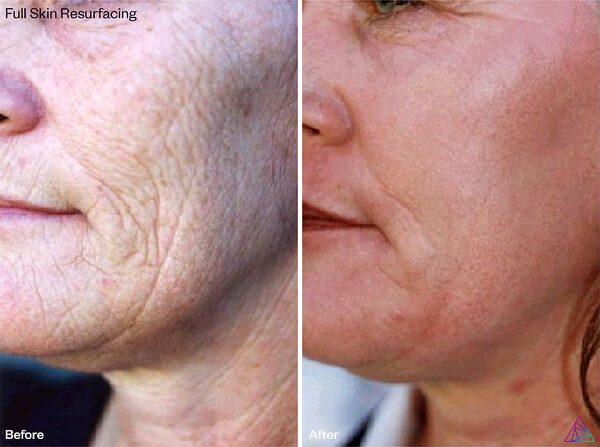
Er:YAG users can very intentionally create treatment protocols specialized for each patient because they have greater control over the thermal damage delivered. By controlling thermal damage, practitioners can administer popular, more superficial treatments with little-to-no downtime such as the “Hollywood Peel” or “Celebrity Peel.” A Hollywood Peel is a light dermabrasion that aims to correct epidermal pigmentation and dull skin. Practitioners typically set pulse duration at only 100 microseconds for “super-cold” ablation. Depending on the treatment style and speed, Er:YAG practitioners can create more or less heat in the skin for added short term collagen tightening.
Thanks to the greatly limited thermal effects of Erbium lasers, Er:YAG treatments are notably less painful than CO2 lasers, and patients do not require any anesthesia when receiving treatment for small lesions. These safety features make Er:YAG lasers the superior choice for treating delicate areas such as the periorbital region, neck, chest, and hands.
4. Erbium:YAG laser treatments have a lower risk of side effects, including hyperpigmentation or skin bleaching, compared to CO2 treatments.
Hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation are mainly due to thermal damage and collagen stimulation. Melanin can only absorb wavelengths between about 300-1,000 nm, so CO2 and Er:YAG do not directly cause the pigment issues. One study* found that hypopigmentation is more likely with CO2 while also finding that treatment depth is related to an increased chance of hyperpigmentation.
While it’s well established that CO2 lasers penetrate deeper in the dermis than Erbium lasers, given constant fluence or energy settings, that doesn’t always correlate with improved patient outcomes. Erbium:YAG lasers deliver impressive results with very few, if any, side effects.
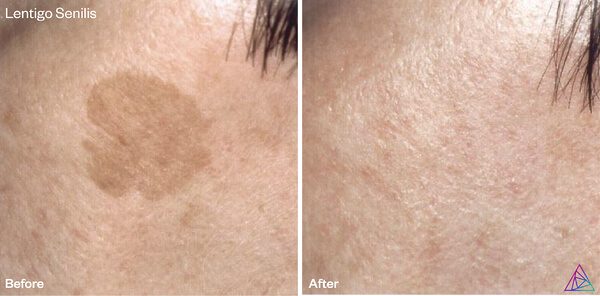
5. Erbium:YAG treatments require a shorter recovery time compared to CO2 lasers.
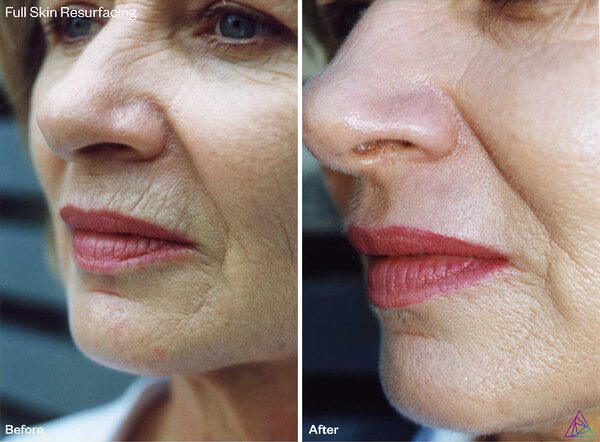
Er:YAG lasers require a shorter recovery time compared to CO2 lasers because of the shallow depths of wounds they create. Furthermore, Er:YAG lasers deliver reduced thermal damage to the surrounding skin tissue, allowing for much faster healing compared to the deeper injuries and extensive thermal damage that CO2 lasers produce.
Although Er:YAG lasers do not penetrate as deeply as CO2 lasers, they’re able to mimic the effects of CO2 lasers by increasing pulse duration while limiting the risk of unwanted side effects. However, a CO2 system can not replicate the same success as an Er:YAG system without increasing the risk of harm to the patient. The flexibility of an Er:YAG laser’s pulse formats and energy capabilities make it a desirable and safer alternative to the time-tested CO2 laser for ablative and fractional treatments.
